Long before the Netherlands became synonymous with tulips, windmills, cheese markets, wooden shoes, Amsterdam’s canals, Old Masters’ masterpieces, Delft Blue earthenware, innovative water management, millions of bicycles, and joyful children, the Dutch were renowned as seafarers, explorers, and conquerors. This small country is packed with world-famous discoveries and inventions. Let’s explore!2. The Microscope
While lenses date back 4,000 years to ancient Greece, the microscope’s invention is attributed to Zacharias Janssen and/or his father, Hans Martens, in 1590. Their prototype magnified objects between three and nine times, initially serving as a novelty.
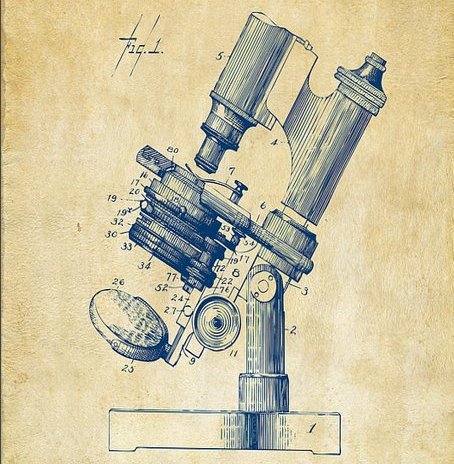
2. Cassette, CD, DVD, and Blu-Ray
In 1963, Dutch giant Philips introduced the cassette. By 1979, they collaborated with Sony to develop the CD. The DVD followed in 1997, and eventually, Blu-Ray emerged, revolutionizing media formats.
3. Bluetooth
On May 7, 1989, Bluetooth technology was introduced by Dutch engineer Jaap Haartsen and Swedish engineer Sven Mattisson at Ericsson in Lund, Sweden. This peer-to-peer wireless technology became a global standard for short-distance connections. The name “Bluetooth” was proposed in 1997 by Jim Kardach of Intel, inspired by King Harald Bluetooth. At the time of this proposal, he was reading Frans G. Bengtsson’s historical novel The Long Ships about Vikings and the 10th-century Danish King Harald Bluetooth.
4. Wi-Fi
In 1991, NCR Corporation, with AT&T, invented WaveLAN, the precursor to Wi-Fi, in the Netherlands. Vic Hayes, known as the “father of Wi-Fi,” chaired the IEEE 802.11 group, leading to the development of Wi-Fi standards. The name Wi-Fi has no further meaning and was never officially a shortened form of “Wireless Fidelity”. Nevertheless, the Wi-Fi Alliance used the advertising slogan “The Standard for Wireless Fidelity” for a short time after the brand name was created, and the Wi-Fi Alliance was also called the “Wireless Fidelity Alliance Inc.” in some publications. WiFi is a short name for Wireless Fidelity. Interbrand also created the Wi-Fi logo. The yin-yang Wi-Fi logo indicates the certification of a product for interoperability.
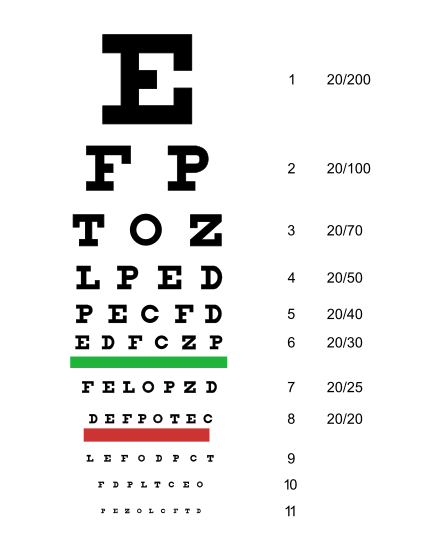
5. The Eye Test
Dutchman Herman Snellen developed the Snellen chart in 1862 to measure visual acuity. This chart, featuring rows of decreasingly sized letters, remains a standard in eye examinations.
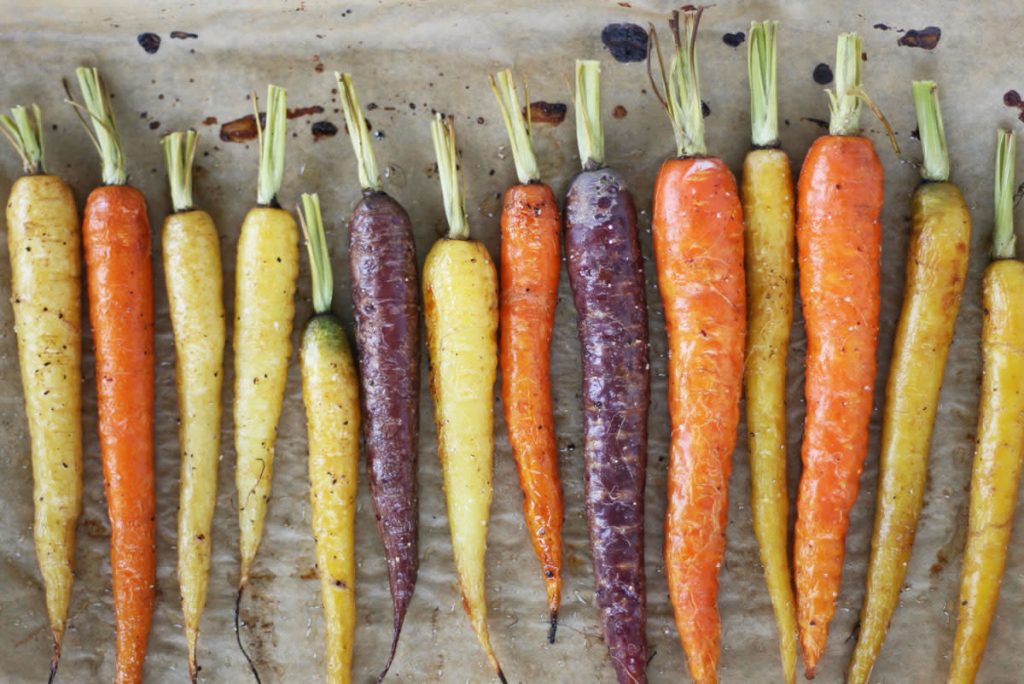
6. Orange Carrots
Who would think that orange carrots were once not orange? Before the 18th century, carrots in Asia were usually purple, while the carrots in Europe were either white or red. Dutch farmers from Hoorn bred orange carrots by crossbreeding pale yellow and red varieties. The House of Orange found them exquisite, leading to their widespread cultivation. The long orange Dutch carrot, first described in 1721, is the ancestor of the orange horn carrot (from the town of Hoorn), one of the most common types found in the supermarket today.

7. Fair Trade
In 1969, the Netherlands opened the first world shop promoting fair trade. The initiative aimed at bringing the principles of fair trade to the retail sector by selling almost exclusively goods produced under fair trade terms in “underdeveloped regions”. The first shop was run by volunteers and was so successful that dozens of similar shops soon went into business in the Benelux countries, Germany, and other Western European countries. By 1988, Dutch proponents introduced the world’s first fair trade label, certifying goods produced under fair trade terms.
8. Elstar Apple
Developed in Elst, Netherlands, in the 1950s by crossing Golden Delicious and Ingrid Marie apples, the Elstar apple is known for its sweet flavor and versatility in cooking and desserts. It quickly became popular, especially in Europe.
9. First Megacorporation – Dutch East India Company
Founded in 1602, the Dutch East India Company, in Dutch Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie or VOC, was the world’s first multinational, joint-stock, limited liability corporation. It issued shares and bonds, establishing the model for modern corporations. The company is often considered by many to be the forerunner of modern corporations. The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was also a major force behind the Golden Age of Dutch exploration and discovery (the 1590s–1720s).

The VOC-funded exploratory voyages. During the Golden Age of Dutch/Netherlandish cartography, VOC navigators, explorers, and cartographers helped shape cartographic and geographic knowledge of the modern-day world. The VOC existed for almost 200 years. During those two centuries, the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asia trade on 4.785 ships and netted for their efforts more than 2,5 million tons of Asian trade goods. Just to have an idea, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882.412 people from 1500 to 1795.
So, how rich was the VOC?
Well, the VOC’s stocks pushed the company’s worth to a massive 78 million Dutch guilders, which is a pretty solid business even today, but translates to a whopping $7,9 trillion dollar worth today! That’s 7.900 billion or 79.000 million! At its peak, the VOC was worth the equivalent of Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, ExxonMobil, Berkshire Hathaway, Tencent, and Wells Fargo put together. This means that the world’s most valuable company.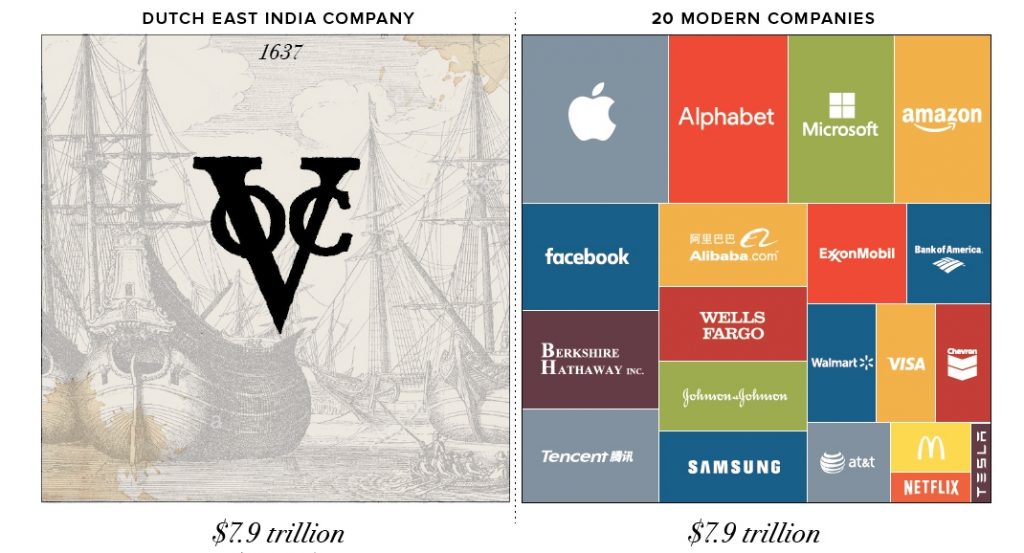
10. The First Modern Art Market
In the 17th century, the Dutch Republic pioneered the modern art market. Artists sold works directly to the public, making art accessible beyond the church and aristocracy. This democratization allowed even farmers and bakers to own multiple artworks.
11. Foundations of the Modern Financial System
The Dutch revolutionized finance by inventing common stock and establishing the Bank of Amsterdam in 1609. They developed key components of modern finance: public credit, stable currency, banking systems, and securities markets.
12. Gin
Dutch physician Franciscus Sylvius is credited with inventing gin in the mid-17th century. Derived from juniper berries, gin evolved from herbal medicine to a popular spirit, especially in Britain during the reign of William III of Orange.
13. Cocoa Powder
In 1828, Dutch chemist Coenraad van Houten developed a method to extract fat from cocoa beans, creating cocoa powder. This innovation made chocolate more affordable and consistent in quality. Van Houten developed the first cocoa powder-producing machine in the Netherlands. 
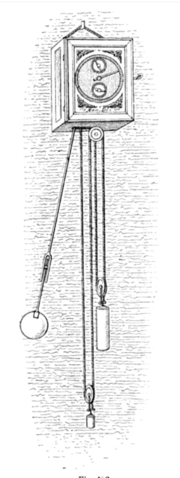
14. Pendulum Clock
In 1656, Dutch inventor Christiaan Huygens created the pendulum clock, based on Galileo’s studies. This invention significantly improved timekeeping accuracy. From their invention until about 1930, the most accurate clocks were pendulum clocks. Pendulum clocks cannot operate on vehicles or ships at sea, because the accelerations disrupt the pendulum’s motion, causing inaccuracies
15. Mercury Thermometer
In 1714, German-Dutch scientist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the mercury thermometer with a standardized scale, enhancing temperature measurement precision.
16. Fahrenheit Scale
In 1724, Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit introduced the temperature scale bearing his name, which became widely adopted, especially in the United States. By the end of the 20th century, most countries used the Celsius scale rather than the Fahrenheit scale. Fahrenheit remains the official scale for Jamaica, the Cayman Islands, Belize, the Bahamas, Palau, and the United States and associated territories.
17. Metronome
In 1812, Dietrich Nikolaus Winkel in Amsterdam invented the mechanical metronome, later patented by Johann Maelzel, aiding musicians in maintaining tempo.
18. Telescope
In 1608, Dutch inventors Hans Lippershey and Jacob Metius filed patents for the telescope. Galileo later improved upon their designs for astronomical observations.
19. Speed Skating
Originating in the Netherlands in the 17th century, speed skating evolved with innovations in skate construction, becoming a competitive sport featured in the Olympics. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marathon speed skating. In the modern Olympic Games, long-track speed skating is usually referred to as just “speed skating”, while short-track speed skating is known as “short track”.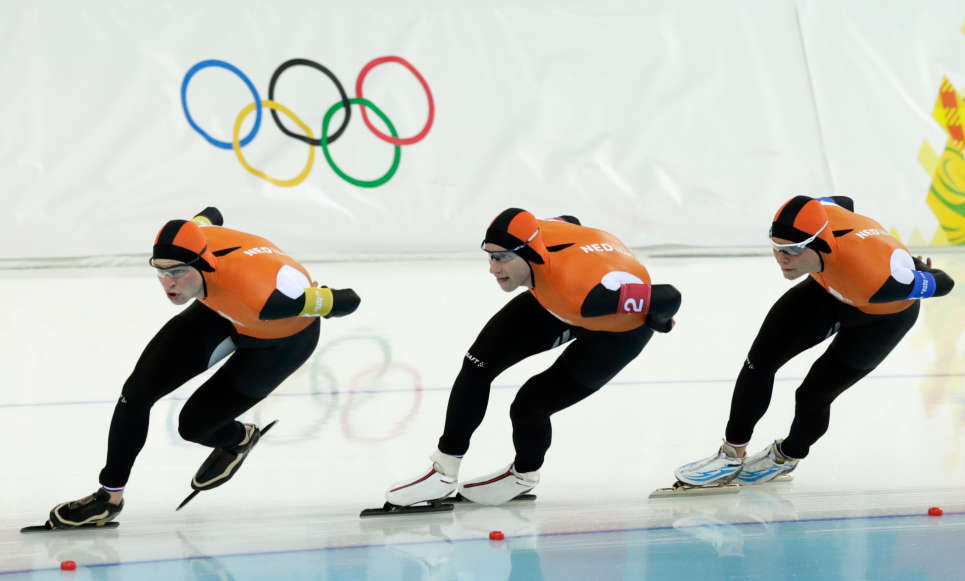
20. Thermostat
Around the 1620s, Cornelis Drebbel developed an automatic temperature control system for a furnace, an early form of the thermostat. He also used this temperature regulator in an incubator for hatching chickens.
21. The Submarine
Cornelius Drebbel designed the first navigable submarine in the early 17th century, successfully demonstrating its capabilities on the Thames River. He designed and manufactured a steerable submarine with a leather-covered wooden frame. Between 1620 and 1624, Drebbel successfully built and tested two more, successively larger vessels. The third model could carry 16 passengers. This model was demonstrated to King James I and several thousand Londoners. The submarine stayed submerged for three hours and could travel from Westminster to Greenwich and back, cruising at a depth of 3.7 to 4.6 m. This submarine was tested many times in the Thames, but never used in battle.

22. Photosynthesis
23. Microbiology
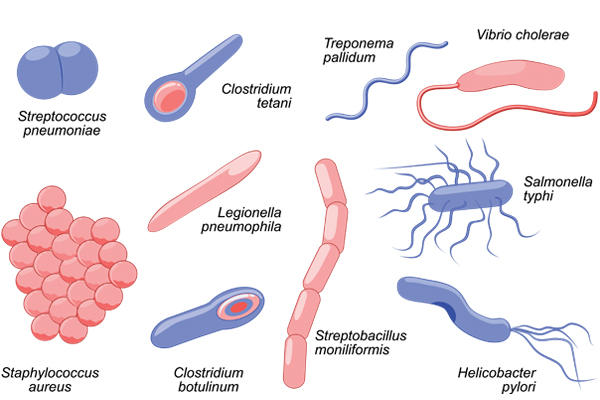
Anton van Leeuwenhoek, using his single-lens microscope, discovered protozoa in 1674 and bacteria in 1676, laying the foundation for microbiology. He also observed sperm cells and Giardia.
24. Discovered Lots of Islands
Dutch explorers like Willem Barents and Abel Tasman discovered numerous islands, including parts of Nova Zembla, Mauritius, Tasmania (originally Van Diemen’s Land), New Zealand, Easter Island, and Samoa, significantly contributing to global cartography.

